We have an app created and linked with our project, so we shall start creating models for our project in order to store the notes details. Here we will create a simple model to store the title and description of our notes.
In the notesapp/models.py add the following code :
from django.db import models
class Note(models.Model):
title = models.CharField(max_length=200)
description = models.TextField()
def __str__(self):
return self.title
This will create a models with two fields, title which is of a CharField , allowing a maximum of 200 chacracters and then a description of the note in a TextField .
After the addition of new models, or after making changes in the fields of a model, you need to run the following commands :
python manage.py makemigrations
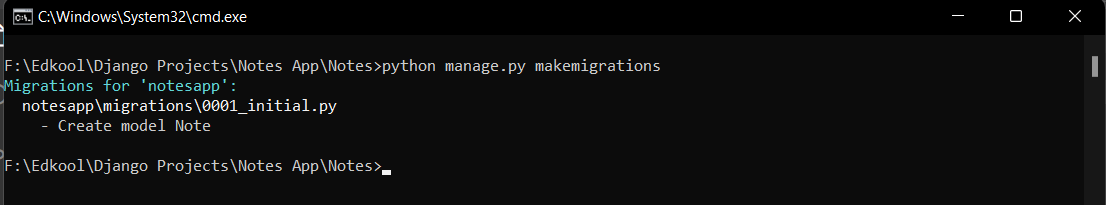 This command is used to generate migration files based on changes you've made to your Django models. These migration files contain a record of the changes you've made to your models (e.g., creating new tables, adding fields, deleting fields).
This command is used to generate migration files based on changes you've made to your Django models. These migration files contain a record of the changes you've made to your models (e.g., creating new tables, adding fields, deleting fields).
After running the makemigrations command you need to run the following command :
python manage.py migrate
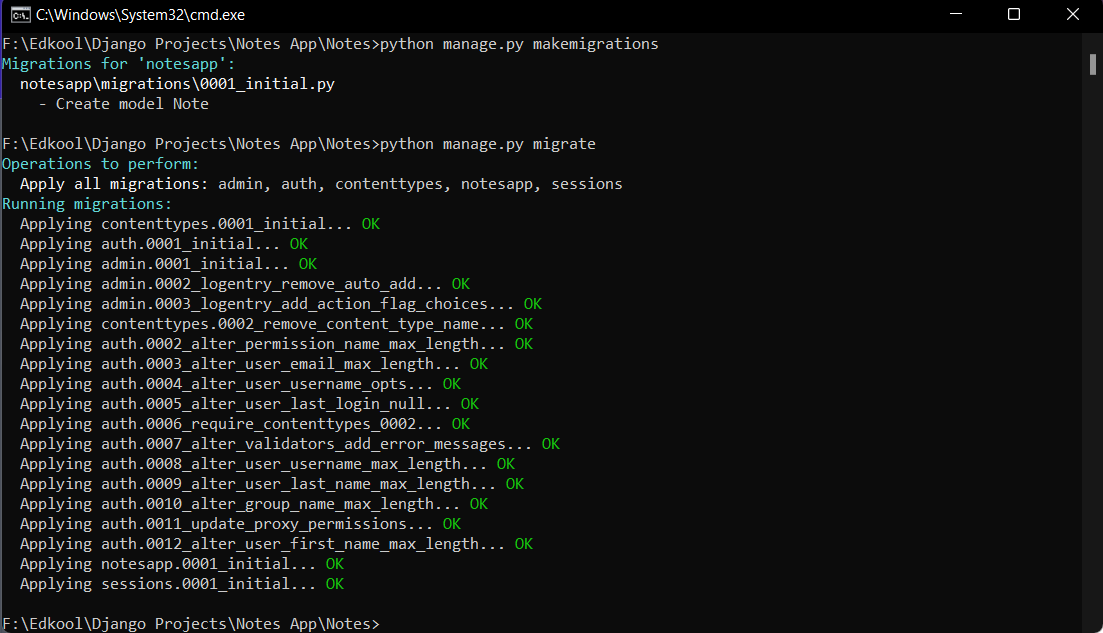 This command is used to apply the changes recorded in migration files to the actual database schema. It takes the migration files created by
This command is used to apply the changes recorded in migration files to the actual database schema. It takes the migration files created by makemigrations and executes them, making the necessary changes to the database.