In Django, the IntegerField is a field type used to store whole numbers (integers). It's commonly used to represent numeric data, such as counts, quantities, or other integer values.
Parameters and Attributes:
-
blank: A boolean parameter that, when set to
True, allows the field to be left blank (i.e., it's not required). The default isFalse. -
null: A boolean parameter that, when set to
True, allows the field to have aNULLdatabase value. The default isFalse. - default: This parameter allows you to set a default value for the field. The default value will be used when creating a new instance of the model if the field is not explicitly set.
-
validators: You can add custom validation functions using the
validatorsparameter to ensure that the data in the field meets specific criteria.
Lets create a model like this,
from django.core.exceptions import ValidationError
def validate_even_number(value):
if value%2!=0:
raise ValidationError(f"{value} should be an even number")
class Demo(models.Model):
STATUS_CHOICES = (
(0, 'Inactive'),
(1, 'Active'),
(2, 'Pending'),
)
field1 = models.IntegerField()
field2 = models.BigIntegerField(null=True, blank=True)
default_value_field = models.SmallIntegerField(choices=STATUS_CHOICES, default=0)
even_number = models.IntegerField(validators=[validate_even_number])
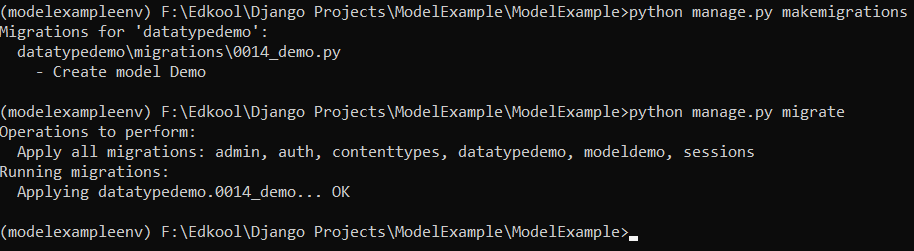
You need to run the python manage.py makemigrations and python manage.py migrate commands to create a model.
python manage.py makemigrations
python manage.py migrate
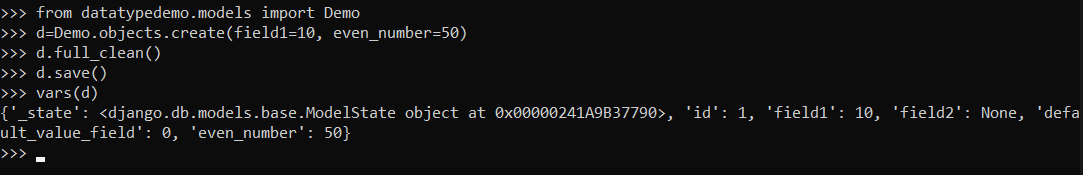
 The model can be accessed as follows :
The model can be accessed as follows :
from datatypedemo.models import Demo
d=Demo.objects.create(field1=10, even_number=50)
d.full_clean()
d.save()
vars(d)
 The
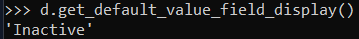
The field2 is None as no value was specified and the default_value_field takes the value 0 as its default value. Also since it is a choice field, you can also view its human readable name as follows :
d.get_default_value_field_display()
 And if you try to assign an odd number to the
And if you try to assign an odd number to the even_number field, you will get a validation error.
d.even_number=1
d.full_clean()
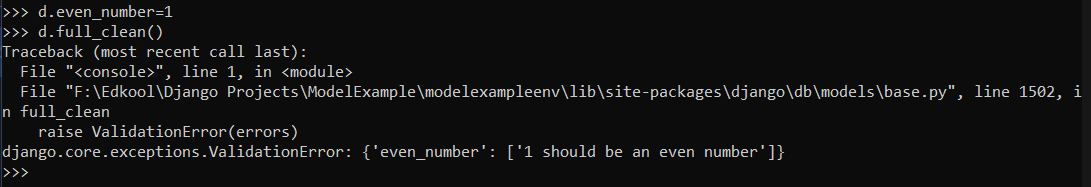 The error would be as follows :
The error would be as follows :
raise ValidationError(errors)
django.core.exceptions.ValidationError: {'even_number': ['1 should be an even number']}
In Django models, there are several integer field types that you can use to represent different ranges of integer values.
-
SmallIntegerField:
-
SmallIntegerFieldis a 16-bit signed integer field. - It can store values from -32,768 to 32,767.
- This field is suitable for situations where you need to store small integers within a limited range, such as status codes, priorities, or ratings.
-
-
BigIntegerField:
-
BigIntegerFieldis a 64-bit signed integer field. - It can store a wide range of large integer values, typically from -9,223,372,036,854,775,808 to 9,223,372,036,854,775,807.
- This field is suitable for scenarios where you need to store very large integer values, such as unique identifiers or large numerical data.
-
-
PositiveIntegerField:
-
PositiveIntegerFieldis a 32-bit signed integer field that only allows positive values (greater than or equal to 0). - It can store values from 0 to 2,147,483,647.
- Use this field when you need to store non-negative integer values, such as counts, quantities, or durations.
-
-
PositiveSmallIntegerField:
-
PositiveSmallIntegerFieldis a 16-bit signed integer field that only allows positive values (greater than or equal to 0). - It can store values from 0 to 32,767.
- Similar to
PositiveIntegerField, this field is suitable for storing non-negative integer values within a smaller range.
-
-
PositiveBigIntegerField:
-
PositiveBigIntegerFieldis a 64-bit signed integer field that only allows positive values (greater than or equal to 0). - It can store very large positive integer values.
- Use this field when you need to store non-negative integers within a wide range.
-
These integer field types in Django models allow you to choose the most appropriate data type for your specific use case based on the range of values you need to store and whether or not negative values are allowed.