The python manage.py runserver command helps you to start the development server, to view in the browser.
You can know more about this command by typing,
python manage.py help runserver
or by typing,
python manage.py runserver --help
On running this command, you will be able to see, how to view the runserver command in different types.
usage: manage.py runserver [-h] [--ipv6] [--nothreading] [--noreload] [--nostatic] [--insecure] [--version]
[--settings SETTINGS] [--pythonpath PYTHONPATH] [--no-color] [--force-color]
[--skip-checks]
[addrport]
Starts a lightweight web server for development and also serves static files.
positional arguments:
addrport Optional port number, or ipaddr:port
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
--ipv6, -6 Tells Django to use an IPv6 address.
--nothreading Tells Django to NOT use threading.
--noreload Tells Django to NOT use the auto-reloader.
--nostatic Tells Django to NOT automatically serve static files at STATIC_URL.
--insecure Allows serving static files even if DEBUG is False.
--version Show program's version number and exit.
--settings SETTINGS The Python path to a settings module, e.g. "myproject.settings.main". If this isn't provided,
the DJANGO_SETTINGS_MODULE environment variable will be used.
--pythonpath PYTHONPATH
A directory to add to the Python path, e.g. "/home/djangoprojects/myproject".
--no-color Don't colorize the command output.
--force-color Force colorization of the command output.
--skip-checks Skip system checks.
By default django would run the development server on http://127.0.0.1:8000/. You can specify a different host and port for running your django project in the following way :
python manage.py runserver 0.0.0.0:80
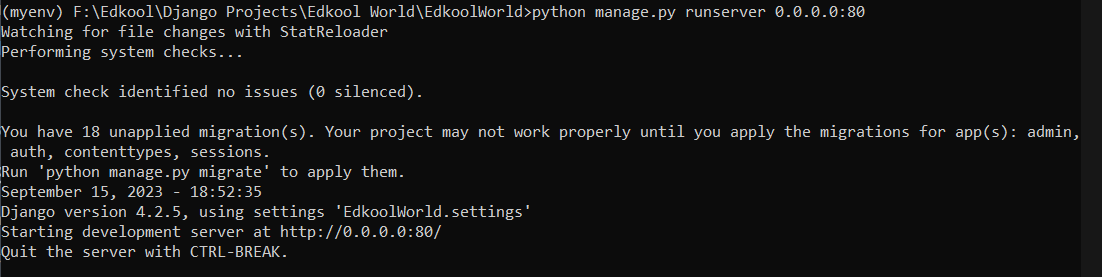 By doing this the host is specified to all hosts, on port 80. So the website can be accessed using http://127.0.0.1/ or http://localhost/ or using the ip address http://ip_address.
By doing this the host is specified to all hosts, on port 80. So the website can be accessed using http://127.0.0.1/ or http://localhost/ or using the ip address http://ip_address.