As the authentication app urls have been linked, we shall create a form to register new users to our website and allow them to submit their details. For this we will create a forms.py file inside the authentication folder and include the form for user registration.
from django import forms
from django.contrib.auth.forms import UserCreationForm
from .models import User
class RegistrationForm(UserCreationForm):
class Meta:
model = User
fields = ('email','first_name','last_name', 'mobile_number', 'profile_photo','password1', 'password2')
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
super(RegistrationForm, self).__init__(*args, **kwargs)
for field_name, field in self.fields.items():
field.widget.attrs['class'] = 'border border-gray-300 p-2 w-full rounded-md focus:outline-none focus:border-blue-500 text-black'
This allows us to take fields of the User Model, and the __init__ function is overrided to set the class of all the fields in the form.
Now we shall create a function to handle the form and pass it through the context.
from django.shortcuts import render
from .forms import RegistrationForm
def register(request):
if request.method == 'POST':
pass
else:
form = RegistrationForm()
return render(request, 'authentication/register.html', {'form': form})
Now, if the request method is not POST, it will display an empty form to the user.
Now the authentication/register.html template needs to be created, for displaying the form.
{% extends 'base.html' %}
{% block title %}
Register
{% endblock %}
{% block content %}
<div class="bg-gray-900 text-white flex justify-center items-center min-h-screen">
<div class="w-full max-w-md mx-4 bg-gray-700 p-6 rounded-md shadow-md">
<h2 class="text-2xl font-semibold mb-4 text-white text-center">Register</h2>
<form method="post" class="form" enctype="multipart/form-data">
{% csrf_token %}
{% for field in form %}
<div class="mb-4">
<label for="{{ field.id_for_label }}" class="block text-gray-300 text-sm font-bold mb-2">{{ field.label }}</label>
{{ field }}
{% if field.errors %}
<ul class="bg-red-500 text-white p-4">
{% for error in field.errors %}
<li>{{ error }}</li>
{% endfor %}
</ul>
{% endif %}
</div>
{% endfor %}
{% if form.non_field_errors %}
<ul class="bg-red-500 text-white p-4">
{% for error in form.non_field_errors %}
<li>{{ error }}</li>
{% endfor %}
</ul>
{% endif %}
<div class="flex justify-center mt-4">
<button type="submit" class="w-full bg-blue-500 hover:bg-blue-700 text-white font-semibold py-2 px-4 rounded-md transition-colors duration-300">
Register
</button>
</div>
</form>
</div>
</div>
{% endblock %}
Here, first a csrf_token is added for security reasons. Next using a for loop, it iterates through each field in the form and displays it. If there are any errors in the form after submitting it, the corresponding errors would also be displayed. At the last a submit button is displayed to handle the form submission.
After making the following code changes, if you run the server along with starting the tailwind, you will be able to view a page like this in http://localhost:8000/register/.
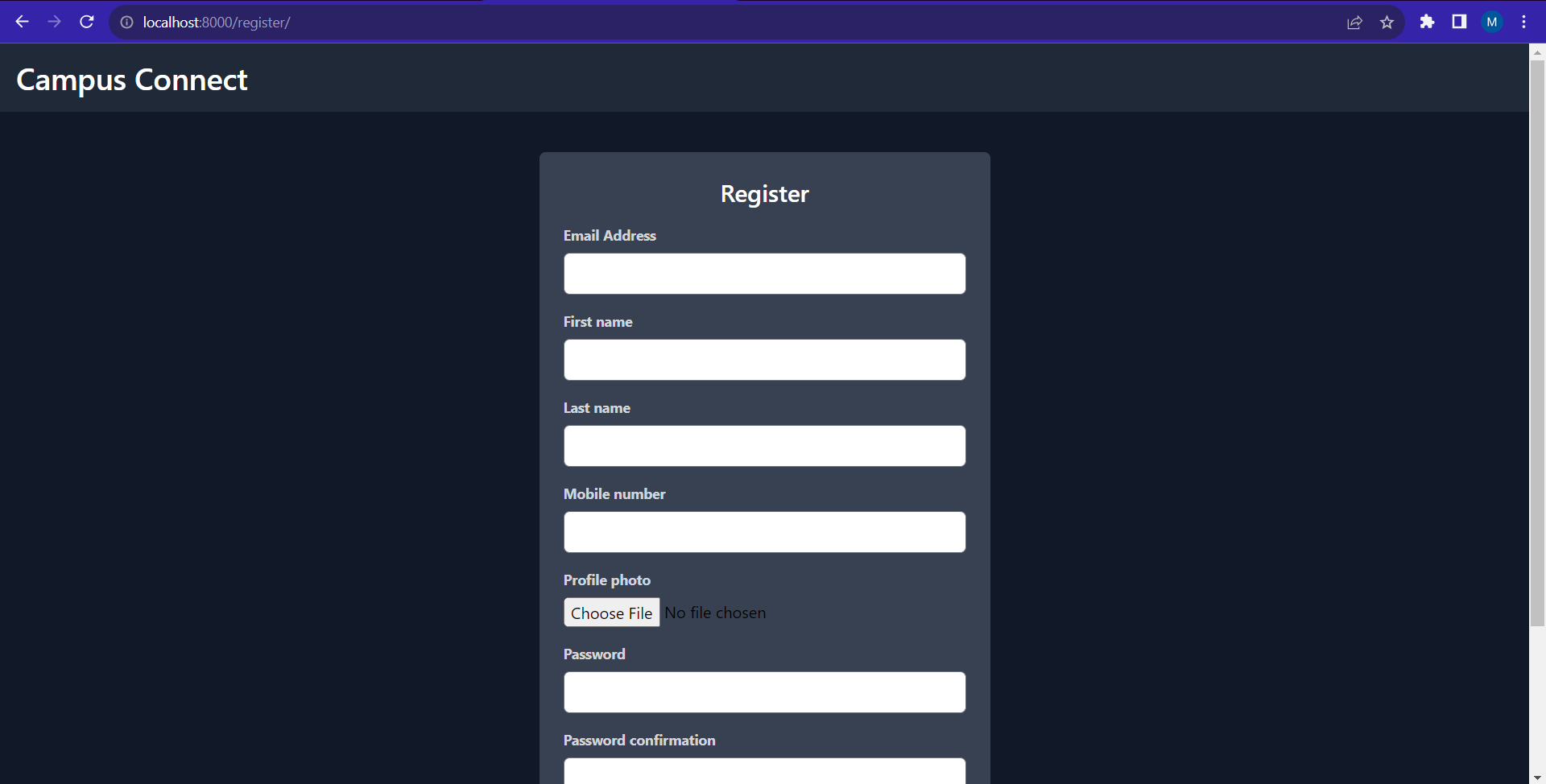 So now, the registration form is being displayed on the page.
So now, the registration form is being displayed on the page.
In the next section, we will handle the form submission and allow the user to login to the website.