In Django, the update() method is used to update one or more records in the database that match a specific set of criteria. Unlike the save() method, which updates a single instance, the update() method operates on a QuerySet and allows you to perform bulk updates efficiently.
Key Points:
-
Bulk Updates: The primary purpose of the
update()method is to perform bulk updates on multiple records simultaneously, which is more efficient than updating each record individually using thesave()method. -
No Signal Handling: Unlike the
save()method, theupdate()method does not trigger any model signals (e.g.,pre_saveorpost_savesignals). This can be an important consideration in some scenarios. -
Field Lookups: You can use field lookups in the
update()method to filter the records you want to update. This allows you to target specific records for modification.
For example, lets say we add another filed in our model, is_active. It would be a boolean field to demonstrate how multiple values can be updated at once. So lets start by making change in our model.
is_active = models.BooleanField(default=True)
After adding this field in the model, you need to run python manage.py makemigrations and python manage.py migrate in order to make changes in the database.
python manage.py makemigrations
python manage.py migrate
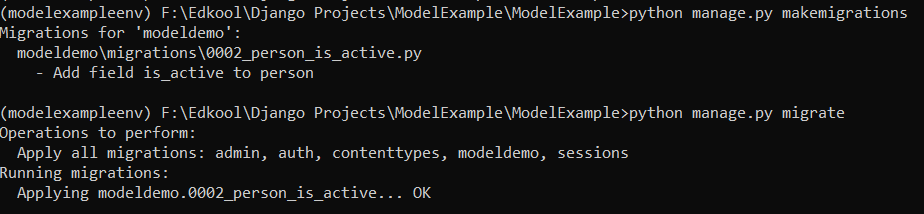 Now the column has been added to the database. If you retrieve the values from the database now, you would also get the
Now the column has been added to the database. If you retrieve the values from the database now, you would also get the is_active column.
vars(Person.objects.get(id=1))
 As you can see the
As you can see the is_active column is present and its default value is True.
Now lets update the is_active value, for all Persons who were born before 1960 to False. You can use the update() method as follows :
Person.objects.filter(birth_date__year__lt=1960).update(is_active=False)
 It will return the number of rows affected, after the update has been performed.
It will return the number of rows affected, after the update has been performed.
You can print and check the rows that have been affected :
Person.objects.filter(birth_date__year__lt=1960).values()
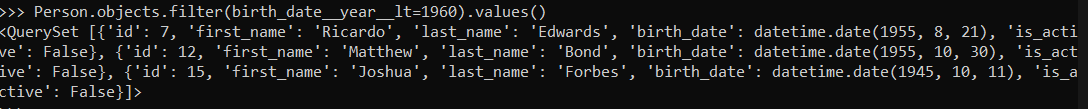 As you can see the
As you can see the is_active column for these rows has been set to False, like this the update() method, can be used to update multiple rows at once.